Clostridium Botulinum and Botulism
A Caitlin, Farida, Nino, Natalie and Simon Presentation
OUTLINE
Introduction to C. Botulinum
Introduction to Botulism
Infant Botulism
Food-Borne Botulism
Wound Botulism
Bioterrorism
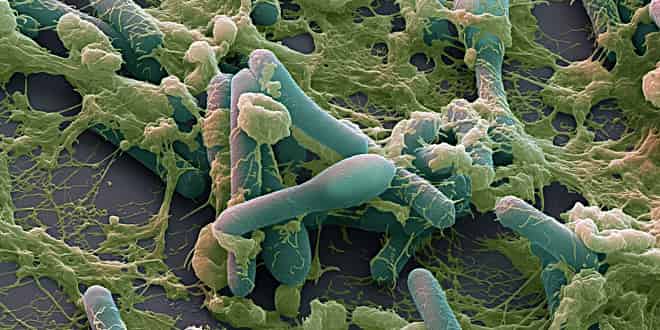
Clostridium botulinum
Gram positive rods
Spore forming
Anaerobic bacteria
Produces toxin that causes botulism
Seven neurotoxic subtypes, labeled A-G
First recognized and isolated in 1896 by Van Ermengem
Botulism
Botulism is a neuroparalytic disease
It is caused by the potent protein toxin released from C. botulinum
Once released into the bloodstream it irreversibly binds to the acetylcholine receptors in the neuromuscular junction
It alters the mechanism for acetylcholine release, making the neuron unresponsive to action potentials
Three major types: Infant, food-borne, and wound
Potential bio-weapon due to its potency
Infant Botulism
Most common form
2 per 100,000 live births in US
Afflicts babies from 1 week – 1 year
Antigenic variations types A/B
Caused by:
Ingesting contaminated foodstuff
Lack of breast milk
Untreated natural honey and corn syrup
Household dust containing C. botulinum spores
Infant Botulism
Signs and Symptoms
Poor feeding (weak sucking)
Weak gag
Weak cry
Decreased movement
Appearing lethargic
Flat, blunted facial expression
Trouble swallowing
Excessive drooling
Muscle weakness
Breathing problems
Ptosis (Drooping eyelids)
Poor head control
Decreased anal sphincter tone
Decreased deep tendon reflexes
Treatment and Recovery
New drug: BabyBIG®, Botulism Immune Globulin Intravenous (Human) (BIG-IV)
Drastically reduces lethargy, IV feeding and overall hospital stay
With early detection, proper treatment, no long term effects observed
Food-borne Botulism
Second most common form
Caused by eating food containing the toxin produced by C. botulinum
Antigenic variations types A/E
Non-commercially canned food is at a higher risk for being contaminated
Dangerous because most contaminated foods cannot be detected until too late
Food-borne Botulism
Signs and Symptoms
12 – 36 hrs after
Muscle weakness,
Diarrhea
Blurred vision
Vomiting
Eventual Paralysis
Treatment and Recovery
Equine Botulinum Antitoxin
Lingering symptoms are fatigue and respiratory difficulty
With early detection, proper treatment, no long term effects observed
Prevention
Inspect canned food for
Bulging
Loose lids
Mold
Odor
Proper home canning procedures:
Hygiene
Time schedule,
Proper processing method
Equipment
Avoiding home canning or cheaply produced commercial food
Wound Botulism
Least common, but on the rise
Occurs when spores inoculate a wound and anaerobic conditions allow germination and subsequent production of the toxin
Associated with IV drug use (rise in black tar heroine use), and medical equipment
-
catheters
Often misdiagnosed as other
neurological syndromes
Bioterrorism
-
botulinum is one pathogenic microorganism that has been researched and developed into a biological weapon.
Many countries, and now terrorists, have developed and used botulinum toxin as a biological weapon.
From 1990 to 1995, aerosols were dispersed at multiple sites in downtown Tokyo and at US military installations in Japan on at least 3 occasions by Japanese terrorists.
In 1995, Iraq revealed that it had deployed more than 11,000 L of botulinum toxin into specially designed SCUD missiles.
Smallpox and anthrax may be
getting the most attention, but
bio-defense researchers have long been concerned about botulinum toxin, the deadliest of all potential toxic threats gram for gram.
A biological attack with the botulinum toxin would more likely be dispersed in an aerosolized form.
Currently, the US military possesses limited quantities of an investigational heptavalent antitoxin, which might be available in the event of a terrorist attack
…